Seleucid Empire - successor state to the Alexander Empire
- Written by Portal Editor
The empire of the Seleucids belonged to the so-called Diadoch states, which had been formed after the death of Alexander the Great by dividing the huge empire of Alexander among its former leaders.
It can be said that the Seleucid Empire extended over the entire territory of the perished Persian Achaemenid Empire excluding Egypt. This extensive area comprised the formerly independent cultural areas of Asia Minor, Palestine, Mesopotamia, Babylonia, Media, Persia and Bactria. During the 3rd and 2nd centuries BC, the Seleucid Empire ruled almost the entire Middle East and extended in its greatest extent from European Thrace to the Indus Valley on the territory of today's states Turkey, Syria, Lebanon, Iraq, Kuwait, Iran, Afghanistan, Armenia, Tajikistan, Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan and Israel as well as the Palestinian autonomous regions.
Expansion of the Seleucids and neighboring states
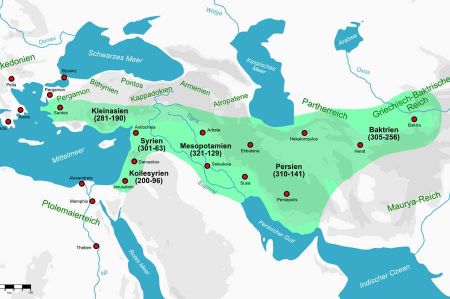
In the west, the Seleucid Empire bordered the Greek motherland and the Macedonian Antigonid dynasty. In the northwest lay the smaller empires of Pergamon, Bithynia, Galatia, Pontus, Cappadocia, Armenia and Atropatene, in the northeast the areas of the nomadic Parthians and the Greco-Bactrian Empire, in the east the Indian Maurya Empire. In the southeast the Seleucids were bounded by the Persian Gulf, in the southwest by the Arabian Nefud desert and the Egyptian Ptolemy dynasty.
Mesopotamia of great importance to the Seleucids
The third focus of Seleucid power was in Sardis in western Asia Minor, where the dynasty 281 BC. could gain a foothold. We had several opportunities to visit the ruins of the former capital Sardis. However, since all the important Diadochian states made claims to the predominantly Greek-populated peninsula, the Seleucids were never able to fully assert themselves here. Their possessions were usually limited to Cilicia bordering Syria and the inland areas of Ionia and Phrygia. Nevertheless, the dynasty regularly tried to gain a foothold in the coastal regions and in Thrace, which is located in Europe. After the defeat by the Roman Empire in 188 BC. however, only Cilicia remained to the Seleucids until the Tauros.
During the early phase of the Seleucid Empire, this comprised from 305 BC onwards. Also the eastern Iranian highlands and the Hindu Kush. The satrapies Parthia and Bactria established there, however, made their way independent around 256 BC. Although nominally they remained Seleucid vassals for a long time, they were never administered directly. Two important empires emerged from Parthia and Bactria, which later extended to Mesopotamia and India, respectively.
In the east, Bactria bordered the Maurya Empire under leader Ashoka. The son of Bindusara sought friendly relations with his neighbors such as the Seleucids and the Greeks in Bactria.
After several generations of decline into a small Syrian state, the Seleucid Empire ended when the Roman general Pompey in 63 BC. deposed the last Seleucid king. To the west of the Euphrates, Rome became the successor of the Seleucids, to the east of it the Parthian Empire.
Please also read:
The imposing Artemis Temple near Sardis
Sardis on Mount Timulus - ancient city with flair
